
The electrostatic force has a horizontal component that results in the leaves moving apart as well as a vertical component that is balanced by the gravitational force. (c) The excess charges are evenly distributed in the stem and leaves of the electroscope once the glass rod is removed.Įlectrostatic repulsion in the leaves of the charged electroscope separates them. (b) When the rod is touched against the ball, electrons are attracted and transferred, reducing the net charge on the glass rod but leaving the electroscope positively charged. Like charges in the light flexible gold leaves repel, separating them. (a) A positively charged glass rod is brought near the tip of the electroscope, attracting electrons to the top and leaving a net positive charge on the leaves. It is typically made with gold foil leaves hung from a (conducting) metal stem and is insulated from the room air in a glass-walled container.
An electroscope is a favorite instrument in physics demonstrations and student laboratories. There, some are transferred to the positive rod by touch, leaving the electroscope with a net positive charge.įigure 2. (Note that the extra positive charges reside on the surface of the glass rod as a result of rubbing it with silk before starting the experiment.) Since only electrons move in metals, we see that they are attracted to the top of the electroscope. Because the glass rod is an insulator, it must actually touch the electroscope to transfer charge to or from it. Charging by Contactįigure 2 shows an electroscope being charged by touching it with a positively charged glass rod. Pure water and dry table salt are insulators, for example, whereas molten salt and salty water are conductors. Electrons and ions in insulators are bound in the structure and cannot move easily-as much as 10 23 times more slowly than in conductors.

Other substances, such as glass, do not allow charges to move through them. In other words, the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons. An ion is an atom or molecule having a positive or negative (nonzero) total charge.
#Insulator definition physics free
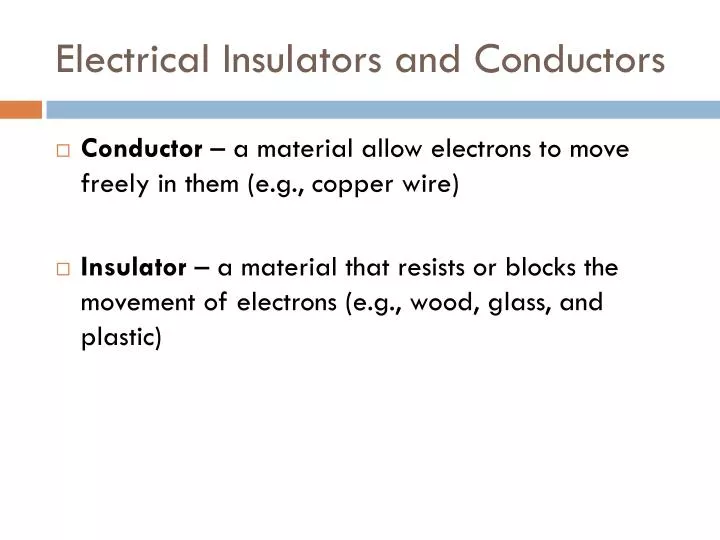
Salty water and other similar conducting materials contain free ions that can move through them. Superconductors allow the movement of charge without any loss of energy. The moving electrons may collide with fixed atoms and molecules, losing some energy, but they can move in a conductor. Any substance that has free electrons and allows charge to move relatively freely through it is called a conductor. These free electrons can move through the material much as air moves through loose sand. Some of the electrons in metals and similar conductors are not bound to individual atoms or sites in the material. Some substances, such as metals and salty water, allow charges to move through them with relative ease. These materials act as insulators that don’t allow electric charge to escape outward. The conducting wires allow electrons to move freely through the cables, which are shielded by rubber and plastic. This power adapter uses metal wires and connectors to conduct electricity from the wall socket to a laptop computer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
